OpenAI’s GPT-4 is powering a new “Deep Search” feature coming to Microsoft Bing. The purpose of the function is to provide users with more thorough and pertinent responses to challenging search queries. Microsoft clarifies that Deep Search is an improvement that enables more in-depth web research rather than a replacement for Bing’s current web search.
Microsoft describes the new feature in a blog post. It improves upon Bing’s existing web index and ranking engine by using GPT-4, which takes the search query and transforms it into a more detailed description of what should be included in the results.
For example, suppose a user types in the query “How do points systems work in Japan” while researching loyalty programs in other nations. The query would be expanded into the following using Deep Search:
Explain the numerous loyalty card programs that are available in Japan, along with their features, requirements, and limits. Provide instances of well-known loyalty cards from various industries, like restaurants, grocery stores, and convenience stores. Compare the pros and drawbacks of loyalty cards with other payment options available in Japan, taking into account the latest offers and incentives. Emphasize the most well-liked offerings and involved retailers.
You can convey your intent more clearly with this extended description than you could have with a few words alone.
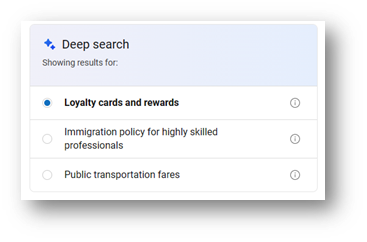
When your search query is more unclear, Deep Search will identify all potential meanings and provide a thorough description for each one. After that, Deep Search shows you these intentions so you may choose the appropriate one.
According to Microsoft, when the enhanced description has been developed, Bing will provide pertinent results that frequently don’t appear in standard search results. After rewriting the question to locate pages that potentially fit the enlarged query, Deep Search looks for those versions as well.
Referring back to the previous example of a loyalty points query, Deep Search may also look for terms like “loyalty card programs Japan,” “best loyalty cards for travelers in Japan,” “comparison of loyalty programs by category in Japan,” “redeeming loyalty cards in Japan,” and “managing loyalty points with online apps.”
Microsoft stated in the blog post that “by doing this, Deep Search can find results that cover different aspects of my query, even if they don’t explicitly include the original keywords.” “Deep Search finds results that are more specific and informative than those that rank higher in normal search, by taking into account ten times the millions of web pages that Bing considers for each search.”
After gathering web pages, Deep Search assigns a ranking to each one according to how closely it matches the enlarged description. Deep Search takes into account several factors when ranking, including how well the topic matches the query, if it has the right amount of facts, the page’s trustworthiness, and how recent and well-liked it is.
Microsoft states that not every query or user should utilize Deep Search because it is optional and can take up to thirty seconds to finish. Users can receive standard Bing search results instantaneously if they don’t want additional in-depth responses.